
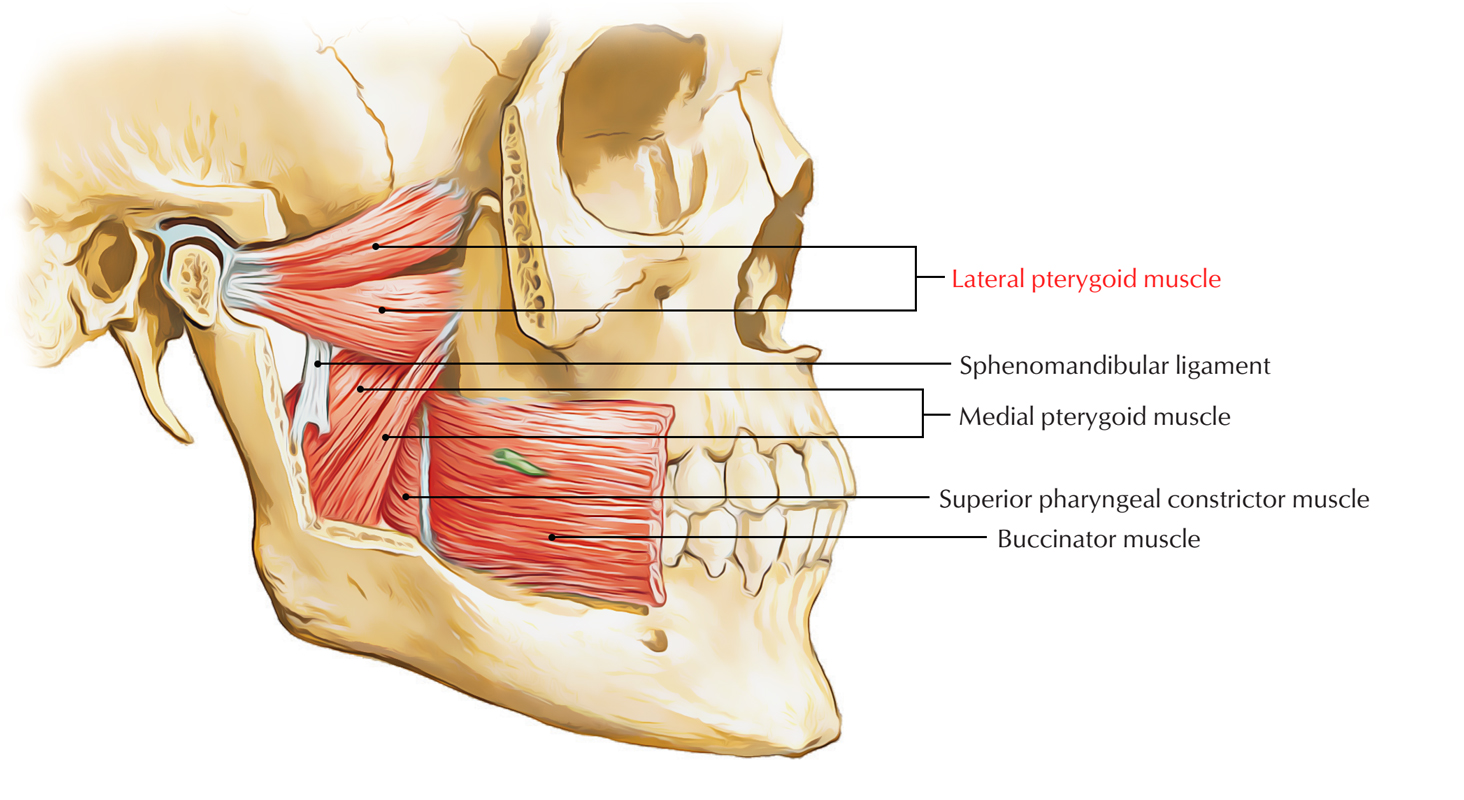
Long-term QoL is independent on radiation dose. The outer circular layer consists of the superior, middle, and inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscles. The middle and lower constrictor should be given special consideration to avoid late dysphagia. Radiation dose to the upper constrictor muscle appears to be of little relevance. Inferior pharyngeal constrictor located in the laryngopharynx. In addition, the pharynx communicates with the nasal cavity, the. Inserts posteriorly into the pharyngeal raphe. The pharynx serves as a continuation of the digestive cavity, providing a route from the oral cavity proper to the esophagus. Originates from the stylohyoid ligament and the horns of the hyoid bone. After 24 months, there was no significant difference (p = 0.374). Middle pharyngeal constrictor located in the laryngopharynx. Late dysphagia is also dependent on the dose level of the middle constrictor muscle (6 months: p = 0.000 12 months: p = 0.005, 18 months: p = 0.034). There were differences 18 months after the end of RT: ≥55 Gy: 19 (86%) patients showed dysphagia grade ≤2 3 (14%) grade ≥3. There was no dose-dependent difference in the severity of dysphagia in the acute phase (p = 0.989). At a dose of <55 Gy, the distribution at the end of radiotherapy (RT) was similar: 22 (69%) patients with dysphagia grade ≤2, 10 (31%) with grade ≥3. At a dose of ≥55 Gy, 14 (64%) patients developed dysphagia grade ≤2 and 8 (36%) patients grade ≥3. Late radiation-induced dysphagia depends significantly on the dose to the lower pharyngeal constrictor. <55 Gy) on late dysphagia and QoL was analyzed using the t‑test. Influence of dose to the constrictors (≥55 Gy vs. The pharyngeal constrictors (superior, middle, and inferior) were each contoured as an organ at risk. Data were collected at standardized intervals using the EORTC questionnaires QLQ-C30 and QLQ-HN35 within two years. 54 patients with locally advanced OPC were evaluated after intensity-modulated radiotherapy. Radiation dose to constrictor muscles plays an important role. The muscles of the pharynx are supplied by the pharyngeal plexus, a network of nerves from pharyngeal branches of the vagus and glossopharyngeal nerves.Patients with oropharyngeal carcinoma (OPC) often have difficulty swallowing, which may affect quality of life (QoL). Most lymph drains back to the retropharyngeal nodes. Veins of the same name drain either into the pterygoid venous plexus or directly into the internal jugular vein. The middle constrictor muscle originates from the greater and lesser horn of the hyoid bone and stylohyoid ligament. When the superior constrictor muscle contracts, it constricts the upper portion of the pharynx. inferior laryngeal artery (from the inferior thyroid artery, off the thyrocervical trunk) The pharyngeal raphe is a midline tendinous seam where the constrictor muscles meet.superior laryngeal artery (from the superior thyroid artery).artery of the pterygoid canal (from the maxillary artery).greater palatine artery (from the maxillary artery).tonsillar artery (from the facial artery).ascending palatine artery (from the facial artery).

ascending pharyngeal artery (from the external carotid artery (ECA)).Numerous branches anastomose in the pharynx, providing it with a rich arterial supply: The internal longitudinal layer is composed of the three paired muscles: The external circular layer is composed of the three constrictor muscles: There are two groups of pharyngeal muscles, the external circular layer and the internal longitudinal layer. communicates with the larynx anteriorly.laryngopharynx (or hypopharynx): inferior to the superior border of the epiglottis and the pharyngoepiglottic folds, superior to the cricoid cartilage.communicates with the oral cavity anteriorly.There are two muscular layers of the pharynx: the outer circular layer and the inner longitudinal layer. oropharynx: posterior to the base of tongue, inferior to the soft palate, bounded laterally by the palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal arches, and superior to the superior tip of the epiglottis The pharyngeal muscles (involuntary skeletal) push food into the esophagus.communicates with the nasal cavity anteriorly.nasopharynx: posterior to the nasal choanae, extending from the vault of the pharynx superiorly to the soft palate inferiorly.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
